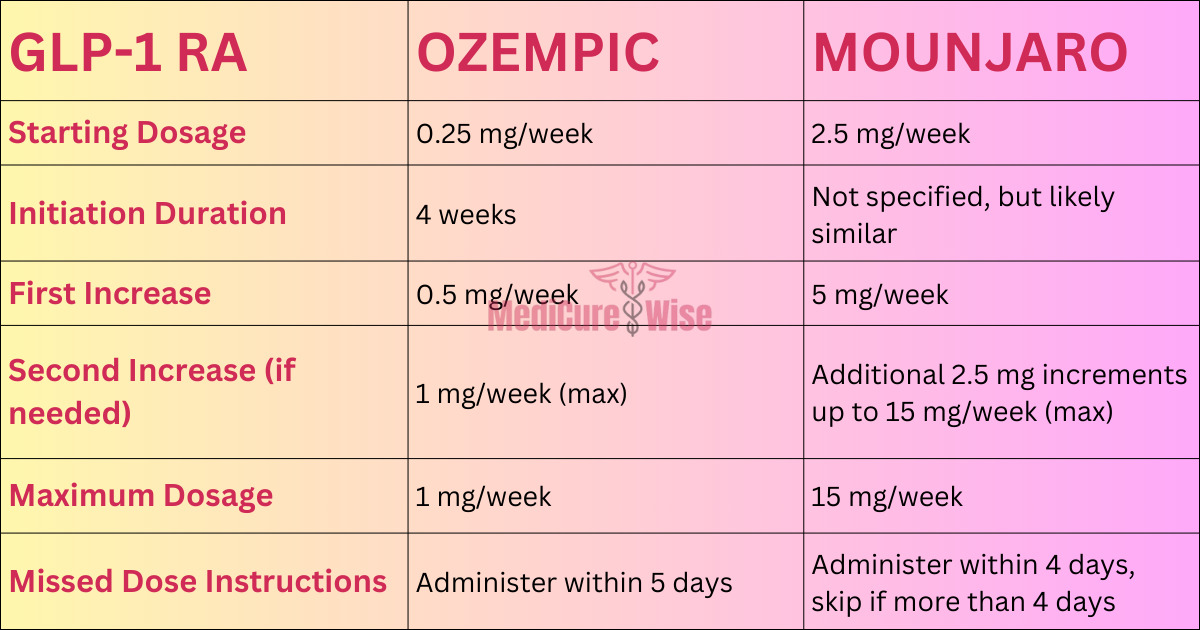
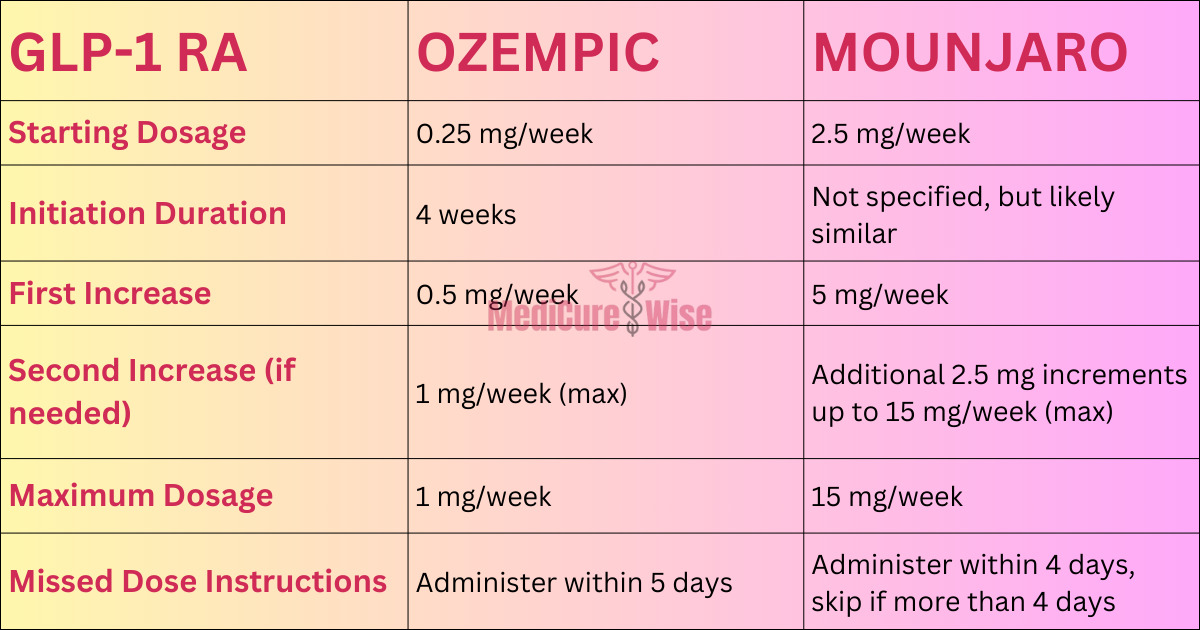
Transitioning from Ozempic’s 0.25 mg/week to Mounjaro’s 2.5 mg/week initiation dose, the following Dosage Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion Chart guides adjustments for glycemic control and weight loss based on individual needs.
| GLP-1 RA | OZEMPIC | MOUNJARO |
|---|---|---|
| Starting Dosage | 0.25 mg/week | 2.5 mg/week |
| Initiation Duration | 4 weeks | Not specified, but likely similar |
| First Increase | 0.5 mg/week | 5 mg/week |
| Second Increase (if needed) | 1 mg/week (max) | Additional 2.5 mg increments up to 15 mg/week (max) |
| Maximum Dosage | 1 mg/week | 15 mg/week |
| Missed Dose Instructions | Administer within 5 days | Administer within 4 days, skip if more than 4 days |
However, accurate conversions require consideration of individual patient factors. It’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for precise guidance, taking into account patient needs and medical history. Official prescribing information or guidelines may offer additional details. Always follow healthcare professionals’ recommendations for safe and effective medication management.
Check out our latest blog for a detailed comparison between Ozempic and Mounjaro. Understanding these differences is key to making informed health decisions.
What are the equivalent doses of Ozempic and Mounjaro?
Discover additional details and the Mounjaro dosage chart on this page.
I. Introduction – Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion Chart
Switching from one diabetes medication to another is a crucial decision influenced by factors such as insurance, cost, side effects, drug availability, and efficacy. In this guide, we will discuss the considerations when transitioning between Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) and Ozempic, shedding light on their mechanisms, benefits, availability, and potential side effects.
If you’re considering a switch from Ozempic(Semaglutide) to Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) and contemplating the possibility of returning to Ozempic, check out my previous blog post on ‘Stopping and Restarting Ozempic‘ for valuable insights and considerations
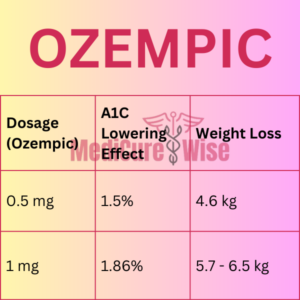
| Dosage (Ozempic) | A1C Lowering Effect | Weight Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 mg | 1.5% | 4.6 kg |
| 1 mg | 1.86% | 5.7 – 6.5 kg |
| Dosage (Mounjaro) | A1C Lowering Effect | Weight Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 2.01% | 7.6 kg |
| 10 mg | 2.24% | 9.3 kg |
| 15 mg | 2.30% | 11.2 kg |
These above two charts can be used alternative to Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion Chart.
REFERENCES FOR DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION OF OZEMPIC to MOUNJARO Conversion Chart.
II. Reasons for Switching
A. Mounjaro to Ozempic
Mounjaro Approval and Limited Experience
Switching from Mounjaro to Ozempic may be motivated by several factors. While Ozempic received FDA approval for diabetes treatment in 2017 and has extensive real-life usage, Mounjaro was approved more recently in 2022 and has limited real-world experience. Ozempic’s wider availability globally adds to its appeal.
Considerations Regarding Side Effects
One significant reason for switching could be the potentially lower occurrence of gastrointestinal side effects with Ozempic compared to Mounjaro. Users of Mounjaro may experience more adverse effects, including pancreatitis, diarrhea, constipation, injection site reactions, and elevated pancreatic enzymes. The increased familiarity with Ozempic and its established safety profile may contribute to a preference for this medication over Mounjaro.
B. Ozempic to Mounjaro
Factors for Switching from Ozempic to Mounjaro:
Switching from Ozempic to Mounjaro may be prompted by several factors. Mounjaro, a twincretin activating both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, offers superior A1C reduction and weight loss. Its availability in some countries and potential as a rescue drug during Ozempic shortages make it an attractive option. Both drugs share a weekly injection schedule.
Side Effects:
Patients may opt for Mounjaro due to its milder side effect profile compared to Ozempic. Ozempic users are more prone to diabetic retinopathy, hypoglycemia, nausea, abdominal pain, and gallstones, potentially driving the decision to switch.
III. Comparison of Side Effects
A. Side Effects Overview
Here’s a detailed table comparing the side effects of Mounjaro and Ozempic:
| Side Effects | Ozempic | Mounjaro |
|---|---|---|
| Contraindications | Allergic reactions | Allergic reactions, MEN II syndrome, Medullary thyroid carcinoma |
| Pancreatitis | – | 13 out of 14 cases |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Varies | – |
| Hypoglycemia | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Acute renal failure | Can cause | Can cause |
| Nausea | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Vomiting | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Diarrhea | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Abdominal pain | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Constipation | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Gallstones | Varies by dose | Varies by dose |
| Amylase | 13% | 38% |
| Lipase | 22% | 42% |
| Injection site reaction | 0.2% | 3.2% |
| Fatigue | 0.4% | – |
| Heart rate | 2 – 3 beats per minute | 2 – 4 beats per minute |
Grateful for insights from Dr. Ahmed, whose expertise in medical field enhances our understanding of Ozempic and Mounjaro in this blog post.
B. Ozempic Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Effects:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Hypoglycemia:
- Low blood sugar levels, especially when used in combination with other diabetes medications or insulin.
- Injection Site Reactions:
- Redness
- Itching
- Swelling
- Bruising at the injection site
- Pancreatitis:
- Inflammation of the pancreas, although this is a rare side effect.
- Diabetic Retinopathy:
- A condition affecting the eyes in individuals with diabetes.
- Gallstones:
- Formation of gallstones in the gallbladder.
C. Mounjaro Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Hypoglycemia:
- Low blood sugar levels, particularly when used in combination with other diabetes medications or insulin.
- Injection Site Reactions:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Itching
- Bruising at the injection site
- Weight Loss:
- Tirzepatide is associated with weight loss, which can be a therapeutic benefit for some individuals but may require monitoring.
- Pancreatitis:
- Inflammation of the pancreas, although this is a rare side effect.
- Renal Impairment:
- Changes in kidney function may occur.
IV. Switching Process
A. Mounjaro to Ozempic Conversion
When switching from Mounjaro to Ozempic, consider the current dose and blood glucose levels. The transition should maintain the weekly injection schedule.
Dose Conversion:
- 2.5 mg Mounjaro: 0.25 mg Ozempic (priming dose)
- 5 mg Mounjaro: 0.5 mg Ozempic (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 7.5 mg Mounjaro: 0.5 mg Ozempic (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 10 mg Mounjaro: 1 mg Ozempic (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 12.5 mg Mounjaro: 1 mg Ozempic (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 15 mg Mounjaro: 1 mg Ozempic (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
B. Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion
When switching from Ozempic to Mounjaro, monitor blood glucose frequently due to Mounjaro’s potency. Consult your healthcare provider for a tailored plan.
Dose Conversion:
- 0.25 mg Ozempic: 2.5 mg Mounjaro (priming dose)
- 0.5 mg Ozempic: 5 mg Mounjaro (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 1 mg Ozempic: 5 mg Mounjaro (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
- 2 mg Ozempic: 5 mg Mounjaro (consider dose adjustment after 4 weeks)
V. Comprehensive Comparison: Mounjaro vs Ozempic
A. Introduction
Mounjaro and Ozempic are medications used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the differences between these drugs is crucial for individuals and healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions.
Significance of understanding the differences
- Mechanism of Action: Mounjaro acts on both GIP and GLP-1 receptors, while Ozempic specifically targets GLP-1 receptors. This distinction may impact the drugs’ efficacy and side effects.
- Treatment Effectiveness: Both drugs are effective in treating type 2 diabetes, but the variations in their mechanisms may influence individual responses.
B. Additional Information
Do Mounjaro and Ozempic Both Lower A1C?
Both Mounjaro and Ozempic are effective in lowering A1C levels. Mounjaro acts on both GIP and GLP-1 receptors, while Ozempic specifically targets GLP-1 receptors. Both drugs have shown effectiveness in blood sugar control and weight loss, as demonstrated in studies like the SURPASS-2 trial. However, Mounjaro has been highlighted in some studies as potentially more effective than Ozempic for blood glucose control and weight loss.
Drug Class Comparison
Mounjaro and Ozempic belong to the same drug class known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications designed to mimic the action of a natural hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). These drugs enhance insulin secretion, reduce glucagon production, slow down gastric emptying, and promote a feeling of fullness, collectively leading to improved blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Administration Methods
Both drugs are administered through subcutaneous injections, typically given once a week. These injections are usually self-administered by the patients, allowing for convenient at-home use.
It’s important to note that while the administration method is similar, there may be variations in the injection technique and site rotation to ensure optimal absorption and minimize injection site reactions. Patients prescribed either Mounjaro or Ozempic should receive proper training on the correct administration procedure from healthcare professionals.
Effectiveness Evaluation
Multiple studies and recent findings suggest that Mounjaro demonstrates greater effectiveness than Ozempic, particularly in terms of weight loss and blood sugar control. According to research published on Fox Business, adults using Mounjaro experienced more significant weight loss compared to those using Ozempic. Another study, mentioned on People, states that Mounjaro is “significantly” more effective for weight loss than Ozempic.
Furthermore, research findings on Health highlight that Mounjaro is more effective for lowering A1C (average blood sugar levels over three months) and weight loss compared to Ozempic. This is supported by studies emphasizing that Mounjaro may be more effective than Ozempic for managing blood sugar levels (Healthline).
While Ozempic remains a FDA-approved and effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, the comparative studies indicate a potential advantage in favor of Mounjaro, especially regarding weight loss and blood sugar management.
D. Price Comparison
Understanding the financial aspects of medication is pivotal. Mounjaro and Ozempic differ in their costs, with variations in dosages and formulations. While Mounjaro’s pricing structure involves different strengths of single-dose pens, Ozempic is priced based on multi-use injection pens. Patients are advised to explore available discounts, insurance coverage, and savings cards to optimize cost management.
- Mounjaro Cost: According to information from Drugwatch.com, specific details about the cost of Mounjaro are not explicitly mentioned. However, cost considerations for Mounjaro may vary and could depend on factors such as insurance coverage and pharmacy pricing.
- Ozempic Cost: Similar to Mounjaro, the exact cost of Ozempic is not provided in the available search results. The cost of Ozempic can be influenced by factors such as the dosage prescribed, insurance coverage, and where the prescription is filled.
- Comparative Analysis: For a comprehensive comparison of the cost between Mounjaro and Ozempic, it is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals, pharmacies, or refer to the official websites of the respective drugs. Cost considerations may involve factors beyond the base price, including the availability of generic versions, discounts, and patient assistance programs.
It’s important to note that medication costs can be dynamic and subject to change, and individual circumstances may impact the overall cost for patients.
E. FAQs
Q. What are the equivalent doses of Ozempic and Mounjaro?
A. Refer to above Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion Chart.
Q.Can I switch from Ozempic to Mounjaro?
A. Switching from Ozempic to Mounjaro is possible, but it can have side effects and should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can evaluate your specific situation.
Q. What is the difference between Ozempic 2mg and Mounjaro 5mg or 15mg?
A. The difference between Ozempic 2mg and Mounjaro 5mg or 15mg lies in their active ingredients, dosages, and mechanisms of action:
Active Ingredients:
- Ozempic 2mg: Contains semaglutide as the active ingredient.
- Mounjaro 5mg: Contains tirzepatide as the active ingredient.
Q. Is Mounjaro stronger than Ozempic?
A. Yes, Mounjaro appears to be stronger than Ozempic based on recent studies and analyses. A large study found that Mounjaro led to more and faster weight loss than Ozempic in overweight or obese adults. Multiple studies indicate that Mounjaro is more effective for weight loss compared to Ozempic. Additionally, Mounjaro has been reported to prompt more weight loss among overweight and obese adults than Ozempic in early trials.
Q. Which is safer Ozempic or Mounjaro?
A. Ozempic has been associated with common side effects such as nausea and gastrointestinal issues, while Mounjaro, being a newer medication, may also have its own set of side effects, including reported cases of abdominal bloating and loss of appetite.
While Mounjaro is reported to be more effective for blood sugar control and weight loss compared to Ozempic, safety considerations should take into account an individual’s health status, medical history, and other factors.
Q. Why is Mounjaro better than Ozempic?
A. Mounjaro is considered better than Ozempic based on various studies and analyses, pointing to its superior effectiveness in blood sugar control and weight loss.
- Effectiveness:
- Numerous studies, such as the SURPASS-2 trial, have indicated that Mounjaro is more effective than Ozempic in managing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss[4].
- Mounjaro has demonstrated better outcomes in terms of weight loss, making it a favorable option for individuals with type 2 diabetes seeking both glycemic control and weight management.
- Side Effects:
- While both medications have side effects, the preference for Mounjaro may stem from its perceived benefits outweighing potential drawbacks, as reported in comparative analyses[5].
- Cost:
- Mounjaro is noted to be more expensive than Ozempic, which could be a consideration for individuals making treatment choices based on cost factors[4].
VI. Conclusion
Switching between Mounjaro and Ozempic requires careful consideration of various factors. This comprehensive guide aims to empower individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, ensuring a smooth transition with minimal complications. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific health needs.
Note: This content is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.